
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Additional chapters in This Section include:
Gender Reassignment Surgery
Orchiectomy for MTF Transsexual Women
FFS Facial Feminization Surgery
MTF Transsexual Surgeries
Hormone Replacement Therapy for Transgender Women
Female Hormone Therapy MTF Transsexuals
Breast Development in MTF Transsexuals
MTF Transsexual Breast Enlargement
Breast Augmentation MTF Transsexuals
Lactation and the Transsexual Woman
Injecting Silicone for Transsexual Women
Brazilian Hips and Buttock Enlargement
Average Body Size MTF Transgender
Male and Female Skeleton Transsexuals
Treatment of Young Transsexuals
Puberty in Adolescents MTF Transgender
Treatment of Young MTF Transsexuals
Treatment of Intersex Infants
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Female Physical Beauty Transgender
Transgender Female Beauty
Exercise, Fitness and Diet for Transsexual Women
I established this page in 2000, it seemed to be generally well received and I incorporated feedback received from various relevant sources. I was thus surprised when in May/June 2003 several ladies with AIS strongly objected to the content. After a careful review I believe that the article is reasonably balanced, and that there are physiological and legal relationships between AIS women and transsexual women that make it appropriate for this site. I appreciate comments from anyone mentioned on this page, and also welcome constructive criticism.
Important Note: Any speculations on this page are my own, and not those of Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Support Group ( |
AISSG
). The text includes amendments made at the request of an AISSG official.
|
Many thousands of women around the world suffer from a disorder known as |
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
(AIS), or in old text books as Testicular Feminization Syndrome. The syndrome is of great interest because it conclusively proves (though perhaps still not to some judges and lawyers) that women can have XY genes, a fact which has considerable significance for genetically XY Male-to-Female (MTF) transsexuals.
|

Women with AIS look and feel like typical women, and in every practical, social, legal, and everyday sense they are women, even though congenitally they have testes and XY chromosomes, and can never bear children. The fact that a "woman" has AIS and is genetically a "male" is often not discovered until puberty, when she does not start to menstruate and a gynaecological examination reveals the syndrome.
(The above two paragraphs are based on material from the literature of the Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Support Group (AISSG).
|

XY Genes - so Boy or Girl?
|
Unlike with MTF transsexual women, no court has ever disputed the right of an AIS woman to legally marry a man and adopt children on the grounds that she's actually genetically XY male. However, an adult AIS woman is physically (internally and externally) almost indistinguishable from a MTF transsexual woman who started surgical and hormonal
treatment before puberty
, so clearly there is a major issue and injustice here.
|
Medical Background of AIS
Every foetus, whether genetically male (XY) or female (XX), starts life with the capacity to develop either a male or female reproductive system. In AIS the child is conceived with male (XY) sex chromosomes and normal embryonic testes (known as the fetal gonads) develop and start to produce masculinizing androgens. However with AIS, a rare genetic condition carried on the X chromosome means that the fetus has no receptors for these male hormones, and his/her body can't "see" or acknowledge them. Lacking the effect of these androgens, the external genitals develop along female rather than male lines. Unfortunately however, another hormone produced by the fetal testes simultaneously suppresses the development of female internal organs (uterus and ovaries).
|

Cindy Stone
has the complete form of Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
.
There are two types of AIS: most (90%) girls have completely normal female type external genitalia, but they lack a uterus or upper vagina. This is known as Complete AIS (CAIS), technically AIS Grades 7 & 6. The remaining girls have Partial AIS (PAIS), their outward genital appearance usually lying anywhere from almost completely female (AIS Grade 5) through to almost completely male (Grade 1).
In PAIS, the foetus showed some response to testosterone (thus the term "partial"). Often girls with partial AIS are born with ambiguous genitalia, where it is not clear at first if the baby is a boy or a girl. If the clitoris is enlarged, it can resemble a small penis, and changes in the labia can make it look like a scrotum. Surgery can be performed to reduce the size of the clitoris, although some experts strongly disagree about when - or even if - the operation should be done. (Clitoral surgery in childhood may interfere with sexual sensation later in life, having a potentially dramatic impact on the girl's intimate relationships as an adult.)
|

All CAIS and most PAIS babies are reared as female because they will:
| have a female type puberty |
| not be able to function sexually as a man but they will be able to do so as a woman. |
In some types of PAIS (AIS Grades 1 & 2) the male genital deformity is so minimal that a baby's gender assignment will be male. Excessive breast development is likely to occur (often unexpectedly!) at puberty, but this can be removed by surgery and some PAIS male may even prove fertile.
|
The most accurate figure available for the incidence of CAIS comes from a 1992 analysis of a Danish patient register, suggesting an incidence of 1 in 20,400 XY births. This includes hospitalized cases only so true incidence is probably higher. PAIS seems to be only about 1/10 as common as CAIS.
|

"Jackie" featured in at least two UK women's magazines in 2004 (pictured from behind or carefully angled). The articles emphasised the mental distress that discovery of an AIS condition causes an otherwise normal teenage girl.
|
Anne Fausto-Sterling
in her excellent book,
Sexing the Body: Gender Politics and the Construction of Sexuality
, suggests that the actual incidence of AIS is about 1 in 10,000 - which would imply up to 3000 people (male and female) suffer with CAIS or PAIS in the UK alone. As support groups and surveys have identified only about 500 such people in the UK, clearly there is still a major hidden problem.
|
Puberty
At puberty girls with AIS experience a
female pubertal development
because their hidden testes produce sufficient estrogen to induce development of the breasts, hips genitalia, etc. (if the testes have been already removed, larger estrogen doses will be given at age 12). The body of an AIS girl not only fails to develop masculinity at puberty, but also develops even further in a feminine direction, causing the body appearance to simulate an adult XX female.
|

Ilizane Broks (age 16) and sister Xenia (6). Ilizane considers herself "more female than male", while Xenia is much more "girlie".
|
Shortly after puberty starts, an orchiectomy will often be performed to remove the testes (primarily to reduce risk of cancer), and Hormone Replacement Therapy begun to substitute for the estrogen that the testes were producing.
|
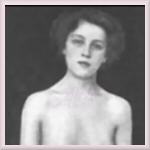 Examples of the physique of AIS woman - warning, potentially offensive.
Examples of the physique of AIS woman - warning, potentially offensive.
In appearance the overall
body shape
typically becomes very decidedly feminine, with a classical female pattern subcutaneous fat distribution and generous breast development - large breasts with pale, under-developed, juvenile appearing nipples are one indication of AIS.
Girls with CAIS will either fail to develop pubic and auxiliary hair (AIS Grade 7), or it remains scant (Grade 6).
Sexual Orientation
Studies
have apparently found that most, although certainly
not all
, women with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (CAIS) have
no problems
with their female gender identity and unambiguously identify themselves sexually as a woman, often leading
normal sex lives
. Statistically their leanings towards heterosexuality, lesbianism or bisexuality may be no different from females in general.
|
 Niamh - a lovely young woman with AIS. She briefly had a website in 1999.
Niamh - a lovely young woman with AIS. She briefly had a website in 1999.
However it must also be recognised that AIS women have both physical and psychological factors that might predispose them to suffer sexual dysfunction, e.g.: shorter than average vaginas, an inability to respond to androgens and anxieties or concerns about their condition, which could impact on self-esteem, body image, sensuality and sexual function. At least one
study
found that sexual dysfunction is common in CAIS, most significantly in the areas of difficulty with vaginal penetration, infrequency and non-communication.
A rough analysis of biographies and articles published on the Internet by or about AIS women shows that while many are married or strongly attracted to men, an unusually large proportion have a
lesbian
or bisexual orientation. But there may well be a bias in these results compared with the actual situation. Speculating considerably, a lesbian or bisexual orientation may be more prevalent in PAIS (rather than CAIS) women where greater social, physical and biological challenges to their female psychosexual sexual identity have occurred at a young age, these problems may have made such women more likely to openly state their situation and adopt an activist position than a far more numerous group of happier and often married heterosexual women who are reluctant to publicize their AIS condition.
 Eden Atwood and her mum. Eden is an actress and wonderful jazz singer, with an amazing life story.
Eden Atwood and her mum. Eden is an actress and wonderful jazz singer, with an amazing life story.
Sex
The external genitalia of a CAIS women are absolutely identical to that of a normal woman, both in appearance, structure and sensations. Given adequate vaginal depth, there is no reason for a CAIS woman and her partner not to enjoy sexual intercourse just as much as any other couple. Things may not be quite so simple for a PAIS woman, but if desired modern feminizing genitoplasty procedures can usually "correct" the external genitalia, again making them indistinguishable from other women.
|
A short, blind-ending, vagina (averaging 5-6 cm long, about half normal size - but with great variance) is present in girls with CAIS, but even this is often lacking in girls with PAIS. Thus before sexual intercourse becomes possible, most girls with AIS must deepen their vagina. In general the best method involves dilation, in which a doctor or nurse teaches the young woman how to use an instrument called a dilator to put pressure on the inside of her vagina. The girl should start dilation only when they feel psychologically ready, usually between the ages of 15 and 20. Over a few months of daily exercises, the vagina becomes deeper and wider, making intercourse possible. Surgical procedures can also be used to lengthen the vagina, but as surgery has more complications than dilation it is avoided if possible.
Some girls and women with CAIS, and almost all of those with PAIS, are born with a partial obstruction to the vaginal opening, and an enlarged penis/clitoris. Before dilation can be safely started they will need a minor surgical procedure to open up the vaginal opening, if this has not already been done. If desired, it is also possible at this time to reduce the penis/clitoris.
Reproduction and Children
Since women with AIS don't have a uterus, ovaries, or eggs there is unfortunately no possibility of menstruation and pregnancy, or her being able to have biological children by any means. Advanced new fertility treatments are starting to offer significant hope for AIS women desperately wishing to have children. Indeed on 24 December 2014,
Hayley Haynes
became the first women with AIS to give birth - and to twins! Extensive hormonal development had stimulated the development of her embryonic uterus, and then in vitro fertilization technology (IVF) used to make her pregnant - donated eggs were fertilized with her husband's sperm and successfully implanted in to her uterus.
|
But realistically, adoption will long remain the most realistic option if a woman with AIS and her husband want to become parents. The use of a surrogate mother is also quite common for those couples with sufficient financial means.
|

11 year old Kylee Whitcher suffers from AIS, pictured with her mother.
|
Appearance
Women with AIS present a typically female appearance (technically, they are phenotypic female). Researchers have
noted
that their body shape does not deviate much from that of normal females but that they tend to be larger in all body measurements, although with a tendency to a slim body. This is thought to be because body shape is controlled by estrogen while the "Y" chromosome is mainly responsible for growth (the absent androgens would have only a small additional effect).
|
Post-puberty, AIS women are typically
tall
for a woman, averaging about 5 feet 7½ inches (171.5 cm), this is just over an inch (3 cm) less than the average man but about 3 inches (8 cm) more than the average woman. However, this average is based on the study of adult women who generally did not have childhood estrogen or HRT treatment. Such treatment can accelerate the completion of growth in the growth plates (the zones of growing cartilage near the ends of children’s bones) of AIS girls, thus helping prevent excessive adult height. The generation of AIS girls currently emerging into early adulthood have often benefited from such early supplemental estrogen therapy and it's therefore presumed that their average height is somewhat less - indeed at least one young woman blames her rather short 5ft 2in stature on excessive early HRT.
 I was kindly sent this picture by an anonymous lady, a tall but attractive appearance is typical of many AIS women.
I was kindly sent this picture by an anonymous lady, a tall but attractive appearance is typical of many AIS women.
There will also be some slight masculinization of the
skeleton
, with proportionally longer legs and arms, and larger hands and feet than the average XY woman, and the size of teeth is closer to men than those of women. [For more information on average male and female body sizes, see the
article
on this site].
Due to the lack of androgen affects the girl will not suffer from acne or temporal hair loss, and little or no pubic hair and auxiliary body hair will develop.
The overall effect is that AIS women tend to be exceptionally beautiful with above average height (for a woman), long and well-proportioned legs, generous breasts, good teeth, exceptionally clear skin and thick scalp hair. According to
one paper
the AIS woman is "often voluptuously feminine", another
report
says "some people with the syndrome look like 'mama mia' women", and even John Money and A. Ehrhardt in their famous book Man and Woman, Boy and Girl noted that AIS girls tend to have a "very attractive female physique".

A glamour shot of actress Jamie Lee Curtis, strongly rumored to have AIS.
|
Unsurprisingly it's been
reported
"because they [AIS women] are unusually beautiful, they are usually found in occupations that pay high salaries for attractive female appearance such as modeling, acting or prostitution".
This is supported by other AIS studies, for example one study found that several top fashion models and two well-known [though unnamed] Hollywood actresses had AIS, an Australian study concluded that "many girls work as models", and another report noted that one of the girls it had studied was an (unnamed) famous photographic model, two were air stewardesses and one a prostitute. "In the old West, women with AIS were reportedly popular among the ranks of prostitutes," notes Vikki Huffnagel, a Californian obstetrician/gynecologist who treats AIS patients. "They were tall, lean, very attractive, and couldn’t get pregnant."
Despite the above comments, it is certainly an extreme exaggeration to suggest that every AIS woman is a potential supermodel; nevertheless it seems that the physiological traits associated with at least CAIS are, on average, likely to increase the attractiveness of a woman with that condition to men.
Famous Woman with AIS
The first historical description of a woman apparently suffering from Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome is in the book Talmud, which dates back to BC400. Other women suspected (based on supposition from limited evidence) to have had AIS include:
|
| Joan of Arc - descriptions of the 'maid' are appropriate to the condition, for example she was twice intimately examined to verify she was indeed a woman but apparently never menstruated; |
| Queen Elizabeth I - descriptions of the 'virgin queen's' appearance, behavior and the physical defects which her contemporaries believed made her sterile and unwilling to marry, all strongly imply a form of AIS; and |
| Mrs Wallis Simpson - from the supposed testimony of her doctor and acquaintances. |

Joan of Arc (Jeanne d'Arc)
|
|

Queen Elizabeth I of England
|
|

Mrs Wallis Simpson and HRH
the Duke of Windsor on their
wedding day, 3 June 1937
|
|

Madonna and Child, by Leonardo da Vinci c. 1482
|
|
Sam Berry, Emeritus professor of genetics at University College London, has also speculated (Daily Telegraph, 21 November 2001) that the Virgin Mary had Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, but with differentiation of her sex organs. He claims that it is possible for a person of this constitution to develop an ovum and uterus, "If this happened, and if the ovum developed parthenogenetically [i.e. unfertilized - common in some animals], and if a back-mutation to testosterone sensitivity took place, we would have a situation of an apparently normal woman giving birth without intercourse to a son."
|
 Elizabeth Short
Elizabeth Short
In America, the notorious Black Dahlia murder case (the basis for a
movie
released in 2006) may sadly be related to a AIS condition. The Black Dahlia (aka
Elizabeth Short
) was a beautiful 22 year-old would-be actress whose body was found horribly mutilated and dismembered in Los Angeles in 1947. The terrible murder has never been solved, but one theory is that the murderer was a suitor who was totally enraged when he found out that she could not have intercourse due to her underdeveloped vagina. It's been claimed that according to people who knew her very well that she never menstruated, but would use a sanitary napkin anyway to help conceal her condition. However the contemporary autopsy doesn't note anything odd about her genitalia, so the question remains open.
As already indicated, medical papers frequently mention that various famous but always unnamed (or pseudonym) actresses and models have AIS. The fires are fanned by semi-reputable sources, e.g. a
link
on
medhelp.org
claims that "there are at least two well-known American movie stars who are XY women", whilst
quiz
questions such as "which Oscar-winning Hollywood superstar’s doctor claims she was born a hermaphrodite, with undescended testes where her ovaries should have been? (and no, it’s not Jamie Lee Curtis)" don't help. [I couldn't help put try to answer this question: the possibilities seem very limited - Charlize Theron, Frances McDormand, Hilary Swank (who have all adopted children) and Renée Zellweger]

Linda Evangelista (left) and Cindy Crawford (right) with actress Bonnie Pfeifer. By 2000 both Linda and Cindy had been pregnant.
|
For obvious and understandable reasons, women with the AIS disorder are very unlikely to admit or confirm that they have it (
Eden Atwood
is a rare and brave exception), while women mistakenly alleged as having AIS are very unlikely to submit to the indignity of medical examinations and karyotype testing for XY genes in order to convincingly disprove it. Nevertheless, speculation and rumour about possible famous women who have AIS is rife in popular magazines, newspapers, and particularly on the web - usually backed up with little or no real evidence other than lack of children. For example, a search of the internet (12 April 2008) suggests as possibly having AIS the ultimate female icon Marilyn Monroe, and other actresses such as Katherine Hepburn, Jessica Biel, Daryl Hannah and
Adriana Catano
. Actress Nicole Kidman also appears, very implausibly given her admission of seeking help for fertility issues - "I’ve done all the stuff you can possibly do to try get pregnant" - and a traumatic miscarriage in 2001.

Hanne Odiele age 27
|
Supermodels are often rumored to have AIS because they fit the stereotype of the syndrome very well - tall, slim, generous bust, wonderful complexion, voluminous hair, big smile, very pretty and attractive, but not delicate and petite. Essentially any top model reaching 35 without children is susceptible to rumors that she has AIS, or is even a transsexual - rumors which are often disproved. For example Cindy Crawford was a victim of the rumor mill in the mid-1990's, but gave birth to a son in 1999 (age 33).
In January 2017, Belgium born model
Hanne Gaby Odiele
bravely
disclosed
that she had AIS in the hope that this would help to break the stigma around the topic and support intersex children. She had her testes removed age 10 to avoid testicular cancer, and surgery to create a vagina age 16. Her slight breast development and other indicators suggest she has partial rather than complete AIS.

|
Actress Jamie Lee Curtis and her sister, Kelly Lee are alleged to suffer from AIS.
|
As already hinted, the actress Jamie Lee Curtis is very frequently cited as an example of a woman with AIS, this is certainly
not confirmed
but there does appear to be an unusual amount of "smoke" in this particular instance. Every time a medical study hints that that unnamed famous actress has AIS, Jamie is always associated. One report
[which I admit I can no longer find]
specifically stated that she was born with Partial AIS (Grade 3), in which case she would have required plastic surgery similar to that undergone by MTF transsexuals to normalize her genitalia as female and create a neo-vagina (Jamie's two children are both adopted).
 Kim Novak
Kim Novak
Finally for this section, the stunningly beautiful movie siren of the 1950's and '60's,
Kim Novak
, is alleged to have AIS. Given her lengthy series of lovers and husbands and the limited surgical techniques available at that time, if true then she was presumably born with Complete AIS and adequate vaginal depth for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
Sport and AIS Women
AIS women are obviously genetically XY male, and allowing them to compete in sports as women has been a source of tremendous controversy since the 1960's. Women with AIS do seem to be either unusually good at sports, or are perhaps more likely to take up sport than other women. Top female athletes have often been found to have AIS when sex tested,
reportedly
1 in 500 women athletes of international standard suffer from AIS, which is an order of magnitude greater than current estimates of about 1 in 5000 AIS women in the general female population. There's considerable competitive interest in this association as it has been
suggested
that Complete AIS represents a valuable model for female performance in sports.
|
Since before the Second World War questions have been raised (sometimes justifiably) regarding the "femininity" of some highly successful female competitors. Initially rather crude visual methods were used to detect male impostors at major sporting events, but from 1968 these were replaced by various tests that verified female gender (or slightly more correctly, physiological sex) by not detecting the presence of either a "male" XY chromosomal pattern or a Y gene. Unfortunately these tests identify as male those athletes who happened to have an XY chromosomal pattern but were otherwise unassailably feminine. AIS women fall in to this category, although ironically their androgen resistance, whether complete or partial, means that unlike other women they are naturally resistant to the strength-promoting qualities of testosterone!
Pumping women athletics full of male hormones was a common practice by the old Soviet block; but it wouldn't work with an AIS woman. "It’s sheer lunacy to think that an AIS woman has an advantage in sports," explains Sherri Groveman, who helps runs an AIS and intersex
support group
"In fact, we’re somewhat at a disadvantage. I could be taking steroids all day long, and unlike other women I wouldn’t develop increased muscle mass. My body can’t respond to androgens."
If AIS women do have any physical advantage in sports then it probably lies in the fact they often tend to be taller and their
skeleton
nearer to male than female in structure, although their musculature and body fat distribution is always typically female.
[Without wanting to argue with Ms Groveman, the author of this article does wonder if this skeletal advantage explains at least some the exceptional success of AIS women in the sporting field. For example, it appears that the average AIS woman is in to the top 10% of the overall female population in terms of height, is it then only a co-incidence that AIS women over succeed at the top level of women's sports by a factor of 10?]
|

Maria Patino, a world class runner, she's now a reporter and coach.
|
In 1985 the 24-year old Spanish hurdler
Maria Jose Martinez Patino
failed a female sex test because of her AIS at the 1985 World University Games in Kobe, Japan. On the way to her first race, she was told that she should fake an injury and withdraw - and if she didn’t, her story would be leaked to the press. She didn’t back down and she won her race, collapsing with physical and mental exhaustion after the finish line. The next day, her story was front page news. She returned to Spain to lose her university scholarship and her boyfriend. “I knew I was a woman in the eyes of medicine, God, and, most of all, in my own eyes,” Patino told a reporter. “If I hadn’t been an athlete, my femininity would never have been questioned". Similarly in the 1988 Olympics an unnamed top women's tennis player was prevented from competing when her condition was similarly identified. In the 1992 Barcelona Olympics 5 out of 2,406 women tested as "male", all with some form of AIS. In the 1996 Atlanta games 8 women out of 3387 didn't pass as female - 4 with CAIS and 3 with PAIS.
However
gender authentication
(sex testing) for athletes had by now become unsustainable. Clearly the vast majority of failures to pass the "sex test" were due to AIS and as no one seriously argued AIS women were not women, the results were effectively false positives. It was also clear that any benefits that an AIS woman may naturally have because of her "male" XY genes are largely offset by the disadvantages of her condition, and at worst are trivial compared with the effects of illegal performance enhancing drugs such as steroids on the genetically XX female body. Finally in February 1999, the Athletes' Commission of the International Olympics Committee urged its parent organization to do away with sex analysis entirely and rely instead on observed urination during drug testing to pinpoint any obvious male impostors.
 Erika Coimbra, pictured three years after the Sydney Olympics
Erika Coimbra, pictured three years after the Sydney Olympics
Mandatory sex testing for women was thus thankfully abandoned for the 2000 Sydney Olympics, but unfortunately considerable
publicity
was still given by the media to two Brazilian women - Judo competitor
Edinanci Silva
and volleyballer
Erika Coimbra
- when it was leaked to the press that both were born hermaphrodites, with non-functioning male genitalia which had been surgically removed. As they actually suffered from AIS they were not banned from competing under the revised rules, but sadly some of their opponents made it known that they were unhappy about this fact - the young, pretty and elf-like Erika (age 20, weight 64kg, height 180cm, with long blond hair) perhaps unsurprisingly receiving much less abuse than the much plainer looking Edinanci (age 24, weight 71kg, height 175cm), whose opponents disgracefully started to refer to as a "he".
In May 2004 the International Olympic Committee dropped all sex testing for
woman's sports
starting with that year's Athens Summer Olympics - with mixed reactions.
Note
: For more information or help regarding AIS, the Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Support Group (AISSG) has an excellent site at
http://www.medhelp.org/www/ais/
. Included among the excellent articles is an
extract
from the book '
Woman - An Intimate Geography'
by Natalie Angier, which in part sensitively considers AIS and the life of one AIS woman.
|
Copyright (c) 2003-2014 Annie Richards
Last updated: 8 July, 2014











 Examples of the physique of AIS woman - warning, potentially offensive.
Examples of the physique of AIS woman - warning, potentially offensive. Niamh - a lovely young woman with AIS. She briefly had a website in 1999.
Niamh - a lovely young woman with AIS. She briefly had a website in 1999. Eden Atwood and her mum. Eden is an actress and wonderful jazz singer, with an amazing life story.
Eden Atwood and her mum. Eden is an actress and wonderful jazz singer, with an amazing life story.
 I was kindly sent this picture by an anonymous lady, a tall but attractive appearance is typical of many AIS women.
I was kindly sent this picture by an anonymous lady, a tall but attractive appearance is typical of many AIS women.




 Elizabeth Short
Elizabeth Short

 Kim Novak
Kim Novak
 Erika Coimbra, pictured three years after the Sydney Olympics
Erika Coimbra, pictured three years after the Sydney Olympics